Telecommunications - Quantum Technology, Quantum Computing, Quantum Security Articles
February 27, 2025
Quantum Use Cases in Telecom
Quantum computing’s impact on global telecommunications will be transformative. It holds the potential to revolutionize how we secure and operate networks, enabling levels of performance and protection previously unattainable. At the same time, it forces a reckoning with the vulnerabilities of our current systems. The journey to fully realize quantum-enhanced telecom will involve overcoming technical challenges and managing risks, but the destination – a world with fundamentally secure, high-capacity communications and perhaps even a quantum internet spanning continents – is one of extraordinary promise ...
Telecom Quantum Readiness: Why the Urgency and Where to Start
An increasing number of telecom leaders have been pinging me lately about quantum readiness. And frankly, that’s exactly what they should be doing. New regulations and mandates are emerging left and right (in various jurisdictions and across the industry) requiring critical infrastructure to become quantum-safe in the coming years. As someone who used to run global telecom cybersecurity practices - and served as interim CISO for several telcos - I can attest that preparing a large telecom for the post-quantum era is far from a trivial “patch update.” In fact, transitioning a telco to post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is an enormous, multi-year effort - likely “the largest and most complex digital ...
Q-Day Isn’t an Outage – It’s a Confidence Crisis
Cybersecurity lore often paints Q-Day (the moment a quantum computer cracks RSA/ECC encryption) as an instant "Quantum Apocalypse" where every system gets hacked immediately. Planes falling from the sky, banks drained in seconds, an overnight digital Armageddon - if that nightmare doesn’t happen, some assume Q-Day wasn’t so bad after all. But this view misses a crucial point. The real catastrophe of Q-Day isn’t that everything will crash at once - it’s that our confidence in all things digital will collapse in an instant. In reality, when quantum code-breaking arrives, nothing visibly “breaks” on day one - websites still load, bank apps still work - yet one of the fundamental ...
Quantum-Readiness / PQC Full Program Description (Telecom Example)
Preparing a large telecom (or any enterprise) for the post-quantum cryptography era is a massive, multi-faceted undertaking, but it is achievable with foresight, resources, and commitment. We’ve seen that it involves much more than just installing new algorithms - it’s about transforming an organization’s approach to cryptography across potentially thousands of applications and devices, under uncertain timelines and in coordination with many external players. In all likelihood, this quantum-readiness program will be one of the most complex IT/security projects the organization has ever executed, comparable to - or even exceeding - major transformations like the rollout of a new network generation or a large merger integration. The program spans technology, ...
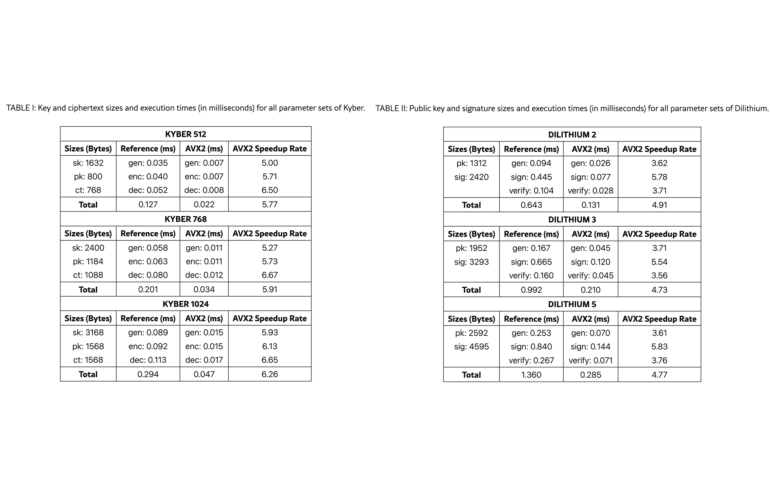
New Study Shows Post‑Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Doesn’t Have to Sacrifice Performance
The new performance analysis of Kyber and Dilithium is a welcome addition to the PQC literature. It confirms that post‑quantum security and good performance are not mutually exclusive, especially when using optimized implementations. In fact, Kyber and Dilithium often outperform classical cryptography at comparable security levels. This challenges the narrative that PQC will drastically slow down our networks. At the same time, the paper reinforces my earlier message: migration is not plug‑and‑play. Larger keys and messages can disrupt protocols and devices, and side‑channel security remains paramount. Enterprises must plan for interoperability, increased memory usage, and hardware support. Hybrid deployments, staged rollouts, and thorough testing are essential ...
Telecom’s Quantum‑Safe Imperative: Challenges in Adopting Post‑Quantum Cryptography
The race is on to quantum‑proof the world’s telecom networks. With cryptographically relevant quantum computers (CRQC) projected to arrive by the 2030s, global communications providers face an urgent mandate to upgrade their security foundations. Today’s mobile and fixed‑line networks rely on public-key cryptography that quantum algorithms could eventually break. In response, the telecom industry is turning to post-quantum cryptography (PQC) as the primary defense. Yet adopting PQC at telecom scale is a complex journey, entailing far more than a simple swap of algorithms. It demands strategic foresight and technical rigor to overcome unique architectural and operational hurdles. As an anecdotal example, my team has been working with one telecommunications provider ...
Cryptographic Bill of Materials (CBOM) for an Open RAN-Based Telecom RAN
Based on anonymized results of a project, I will try to illustrate key parts of a comprehensive Cryptographic Bill of Materials (CBOM) for a telecom Radio Access Network (RAN) implementation based on the Open RAN architecture. I enumerate all cryptographic mechanisms across the control plane, user plane, management interfaces, and orchestration layers of the RAN. Both standardized algorithms (e.g. 3GPP-defined ciphers like SNOW 3G, AES, ZUC) and any vendor-specific/proprietary mechanisms are included, with an emphasis on an EU deployment scenario. In the European context, strong encryption and security-by-design are mandated; for example, ENISA (the EU cybersecurity agency) recommends using non-null ciphers for all user and signaling data and state-of-the-art protocols with ...
Is 5G security being sacrificed at the altar of profit, politics and process?
Homo sapiens is an incredibly adaptable species, arguably the most adaptable ever. But it is also a forgetful one, quick to take things for granted. Many of us can remember when cell phones first emerged, when the internet first became publicly available, when the first iPhone was released. These momentous shifts occurred within a generation, altering the nature of society and civilization. Just a few decades ago, none of these existed, but by the time Covid-19 hit, billions of people were able to lift their smartphone and video call a loved one on the other side of the world. At the time, few people seemed to pause and recognize that ...
Quantum Readiness for Mission-Critical Communications (MCC)
Mission-critical communications (MCC) networks are the specialized communication systems used by “blue light” emergency and disaster response services (police, fire, EMS), military units, utilities, and other critical operators to relay vital information when lives or infrastructure are at stake. These networks prioritize reliability, availability, and resilience – they must remain operational even during disasters or infrastructure outages. For example, in a hurricane that knocks out commercial cell towers and power, robust MCC networks are expected to “rise above” the chaos and keep first responders connected. Communications security is equally paramount: in crisis scenarios, sensitive information (tactical plans, personal data, etc.) must be protected from interception or tampering, even as the ...
Can we afford to keep ignoring Open RAN security?
I’m skeptical of ‘futurists’. Work closely enough with the development of technology solutions and you’ll know that the only certain thing about the future is that it’s constantly changing. For example, few ‘futurists’ predicted the Covid-19 outbreak that brought the world to a standstill in 2020. Many, however, had spent hours waxing on about how 5G technology was to change the trajectory of human evolution, telling tales of what would be possible with ultra-high speed, ultra-low latency connectivity. Me included. Of course, 5G will enable many of these promised use cases, and many others we haven’t even dreamed of yet, but have the prophets been proven true? Has 5G changed ...
Cryptography in a Modern 5G Call: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Modern telecommunications networks rely on multiple layers of cryptography at every step of a call or data session. Understanding the complexity of the process and the amount of cryptography involved is critical for post-quantum migration planning - an initiative some of my advanced telecommunications clients are kicking off these days. And many are widely underestimating how much cryptography is used. From the moment a user’s device connects to the network, through call setup (or SMS delivery), across roaming interfaces, and into backend billing, dozens (hundreds?) of cryptographic mechanisms are at work ...