My Articles, Opinions and Analyses
Bitcoin’s Quantum Timeline Is Not RSA’s Quantum Timeline
Most quantum-risk-to-Bitcoin analyses rehash RSA-2048 timelines. They're missing the point. Bitcoin doesn't use RSA. It uses 256-bit ECC - and Shor's algorithm will break that first. Scan the quantum computing coverage of Bitcoin and you will find a remarkable pattern. Article after article cites the same RSA-2048 qubit estimates - 20 million physical qubits (Gidney-Ekerå ...
Q-FUD: The Quantum Panic Industry
Cybersecurity has always had a FUD problem. “FUD” (fear, uncertainty, and doubt) is the oldest trick in enterprise security marketing: paint a worst-case scenario, imply you’re already compromised, sprinkle in enough jargon to make the buyer feel outgunned, and then offer the “only” solution - conveniently available this quarter. Q‑FUD is that same playbook, just ...
Quantum Low-Density Parity-Check (qLDPC) Codes
Quantum Low-Density Parity-Check (qLDPC) codes are an emerging class of quantum error-correcting codes that promise to significantly reduce the overhead required for fault-tolerant quantum computing. Much like their classical LDPC counterparts, qLDPC codes are defined by sparse parity-check constraints: each check (stabilizer) acts on only a small number of qubits, and each qubit participates in ...
Pinnacle Architecture: 100,000 Qubits to Break RSA-2048, but at What Cost?
Iceberg Quantum's Pinnacle Architecture paper claims RSA-2048 can be factored with fewer than 100,000 physical qubits - a genuine 10× reduction over the previous state of the art - by replacing surface codes with quantum LDPC codes. The result is credible but shifts difficulty from qubit count to equally daunting engineering challenges: non-local connectivity, fast ...
Payments and the Race to Quantum Safety / Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
The payments industry has navigated big cryptographic transitions before. The migration from magnetic stripes to EMV chips took the better part of two decades and cost billions. The shift from SHA-1 to SHA-256 certificates was painful but bounded - it mostly meant updating software, not ripping out hardware. The post-quantum transition is different in kind, ...
120,000 Tasks: Why Post‑Quantum (PQC) Migration Is Enormous
When I tell fellow CISOs, board members, or even seasoned program managers that the integrated program plan for a comprehensive quantum security / post-quantum cryptography (PQC) migration I recently worked on contained over 120,000 discrete tasks, the reaction is almost always the same. First, there is a polite silence. Then, the inevitable furrowing of the ...
QuantWare
QuantWare is a Delft, Netherlands-based quantum computing startup that provides superconducting quantum processors as off-the-shelf products. Founded in 2021 as a spin-out from TU Delft’s QuTech institute by Matt Rijlaarsdam and Alessandro Bruno, the company aims to be the “Intel of quantum computing” by supplying affordable, high-quality quantum QPU (quantum processing unit) chips for others ...
China Just Pushed Device-Independent QKD (DI-QKD) to 100 Kilometres
A team at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) published a paper in Science that quietly redrew the map of what device-independent quantum key distribution (DI-QKD) can do. Led by Bo-Wei Lu, Chao-Wei Yang, Run-Qi Wang, Xiao-Hui Bao, and the ever-present Jian-Wei Pan - the physicist sometimes called China's quantum communications supremo ...
Quantum Open Architecture (QOA): The “PC Moment” of Quantum Computing
Today, a sea change is underway. Quantum Open Architecture (QOA) is doing for quantum computing what the PC revolution did for classical computing - opening up the ecosystem. Just as the computing world shifted from monolithic mainframes to modular PCs with swappable parts, quantum tech is embracing modularity and specialization. Instead of one vendor building ...
Quantum Sovereignty in Practice: When Geopolitics Becomes Architecture
At its core, quantum sovereignty means having full control over the critical layers of quantum technology domestically - the ability to design, manufacture, and operate quantum systems without external dependency. In practice, this implies a country could build a complete full-stack quantum ecosystem entirely within its national borders: from quantum chips and cryogenic hardware to ...
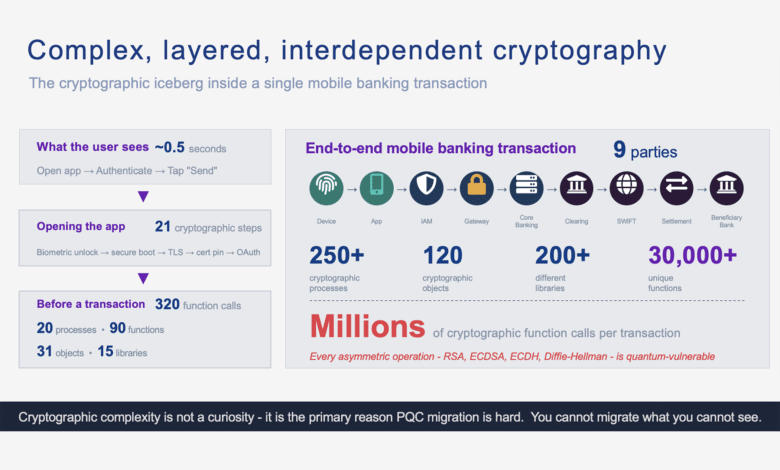
The Cryptographic Iceberg Inside a Mobile Banking Transaction
A single mobile banking payment triggers millions of cryptographic function calls across nine parties. Here's what actually happens - from silicon to settlement - and why it matters for quantum readiness. The Cryptographic Iceberg Inside a Mobile Banking Transaction 320 function calls before you even type an amount It takes roughly half a second. You ...
NIS2, DORA, and the EU Post-Quantum Roadmap
If you are a CISO under NIS2 or DORA, you are already expected to run a risk-management system that tracks material, evolving threats - and to implement “state‑of‑the‑art” controls appropriate to the risk. The EU’s PQC roadmap is effectively saying: quantum is now one of those evolving threats you must govern. The most important conceptual shift ...
The Complete US Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Regulatory Framework in 2026
Three pillars anchor the US PQC framework: the Quantum Computing Cybersecurity Preparedness Act (federal law that no executive order can undo), NSM-10's 2035 migration target (still in force), and NIST's finalized FIPS standards (published August 2024). The Trump administration's June 2025 executive order streamlined, rather than eliminated, PQC obligations, removing prescriptive procurement mandates while retaining ...
No Single Law, No Single Excuse: How Canada Regulates PQC Without Saying “Quantum”
Canada's visible PQC guidance - three documents published mid-2025 - is just the tip. Beneath it sits a layered enforcement framework spanning financial regulation, critical infrastructure law, privacy obligations, and securities disclosure that collectively creates binding pressure for quantum readiness. OSFI already requires federally regulated financial institutions to maintain "strong cryptographic technologies" and has issued ...
Telecom Quantum Readiness: Why the Urgency and Where to Start
An increasing number of telecom leaders have been pinging me lately about quantum readiness. And frankly, that’s exactly what they should be doing. New regulations and mandates are emerging left and right (in various jurisdictions and across the industry) requiring critical infrastructure to become quantum-safe in the coming years. As someone who used to run ...
How the EU Can Capture the Benefits of Quantum Computing
The European Union has entered the global quantum race with determination - aiming not just to excel in research, but to translate breakthroughs into economic and strategic benefits. In July 2025, the European Commission unveiled the Quantum Europe Strategy, a roadmap to make Europe a “quantum industrial powerhouse” by 2030. This strategy acknowledges Europe’s historic ...
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Why Countries Differ on Its Future
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) - a method of securing communications using quantum physics - has become a flashpoint of debate worldwide. Recent news (like Google’s announcement favoring post-quantum algorithms over QKD) highlights how divided opinions are. Some nations are investing heavily in QKD networks as the next frontier of secure communications, while others remain skeptical ...
Q-Day Knowledge Center & Q-Day Framework and Estimator
Q-Day Knowledge Center - Your complete guide to understanding, forecasting, and preparing for quantum decryption risk ...
Sovereignty Stress Tests: Tabletop Scenarios for States and Enterprises
In an era of quantum and digital sovereignty, governments and companies must ensure they aren’t caught off-guard by geopolitical tech disruptions. Building on my previous analyses of quantum sovereignty and a number of Applied Quantum client engagements, I wanted to offer a practical scenario toolkit to “stress test” sovereignty. Instead of chasing total self-sufficiency, the ...
Rethinking CBOM
The simplest way to explain CBOM is still the best. If SBOM is the ingredients list for software, CBOM is the ingredients list for the security assumptions that software depends on. Where SBOM tracks components and dependencies, CBOM tracks cryptographic assets - algorithms, protocols, certificates, keys, and related material - and the relationships that turn ...
Experimental Quantum Error Correction Below Threshold
When Harvard’s neutral-atom team quietly dropped their new paper on a fault-tolerant architecture for universal quantum computation, a few days ago, it felt like the field had crossed an invisible line. For years we’ve had impressive pieces of the puzzle - better qubits here, a clever code there, some elegant theory everywhere – but Lukin’s ...
Investment Screening and M&A: When Capital Becomes a Quantum Sovereignty Vector
Foreign investment screening, acquisition scrutiny, and “strategic capital” policies increasingly shape which quantum technology companies survive - and where their intellectual property (IP) and talent ultimately reside. National security and technological sovereignty narratives are no longer abstract concerns; they influence the day-to-day decisions of quantum startups. The Sovereignty Stakes in Quantum Investment Quantum technologies are ...
Quantum Sovereign Optionality: Agility Over Autarky
Technical sovereignty has become a buzzword in geopolitical and tech circles. As global alliances fray and trust in traditional partners wanes, countries are scrambling to assert control over critical technologies. In the quantum arena, this instinct translates into an ambitious goal: build a complete, full-stack quantum ecosystem entirely within national borders. The allure is understandable ...
Silicon Quantum Computing
Silicon Quantum Computing (SQC) is an Australian quantum hardware company based in Sydney, founded in May 2017 as a UNSW Sydney spin-off by Prof. Michelle Simmons (2018 Australian of the Year). It was launched as Australia’s first quantum computing company with A$83 million in seed backing from the Australian government, UNSW, Telstra, Commonwealth Bank (CBA), ...