99.5% Fidelity in Neutral-Atom Qubits Achieved
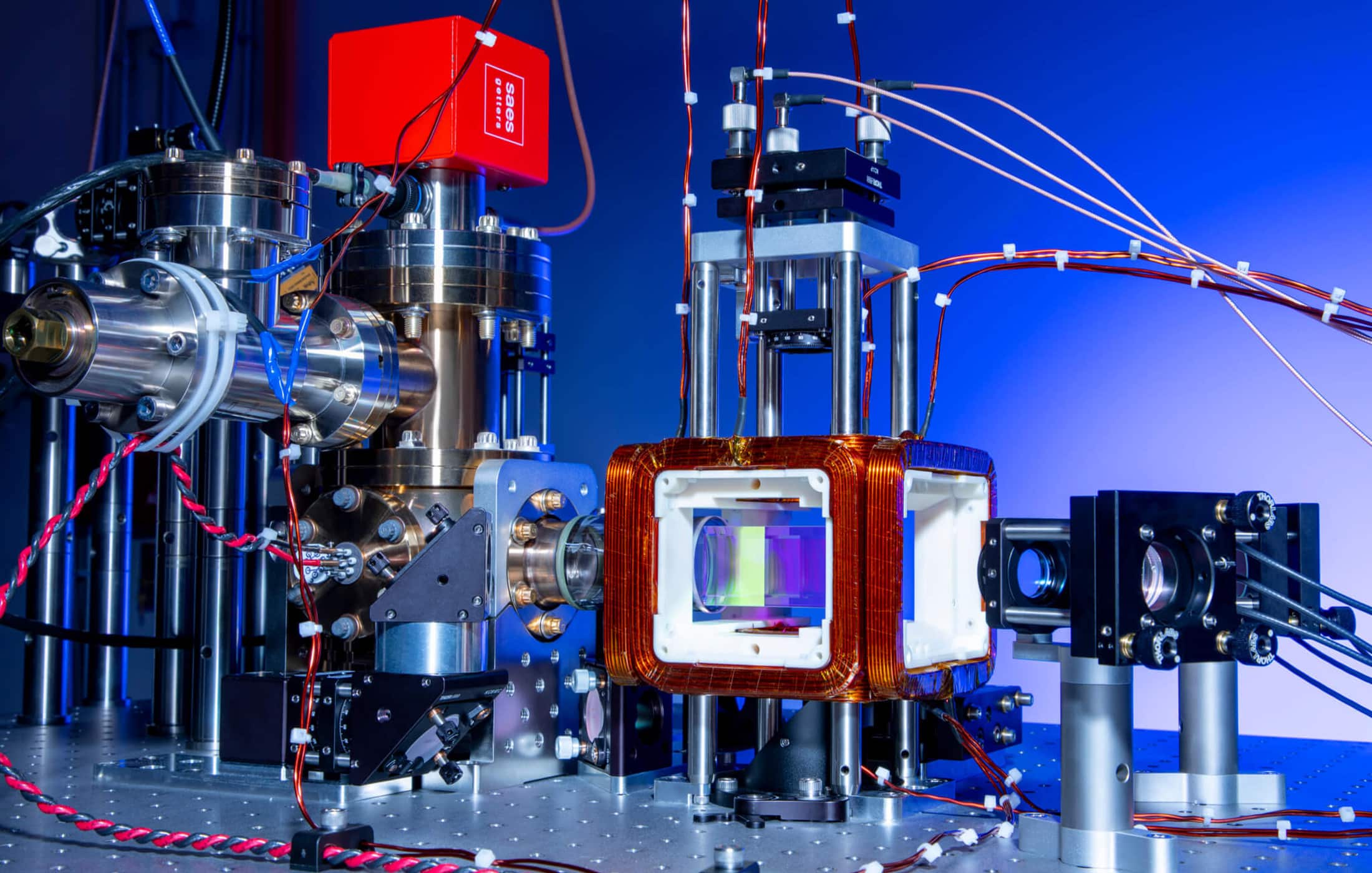
A team of researchers from Harvard University, MIT, and QuEra have achieved two-qubit entangling gates with 99.5% fidelity on 60 neutral atom qubits operating simultaneously. This milestone represents a crucial step towards the practical application of quantum computing in commercial environments.
The collaborative research signifies a major leap forward in the quest for reliable quantum information processing. Detailed findings from this research are available in a paper published on ArXiv.
Neutral atom arrays have recently gained recognition as a promising quantum computing platform, thanks to their capability for coherent control over large numbers of qubits and their flexible, dynamically reconfigurable architecture. Achieving high-fidelity operations is essential for surpassing quantum error-correcting thresholds, a prerequisite for the effective deployment of quantum technologies.
For more detailed insights, the complete research paper is accessible on ArXiv: High-fidelity parallel entangling gates on a neutral atom quantum computer.



