Post-Quantum, PQC, Quantum Security
PostQuantum.com – Industry news and blog on Quantum Computing, Quantum Security, PQC, Post-Quantum, AI Security
-
The Trouble with Quantum Computing and Q-Day Predictions
The trouble with quantum computing predictions so far has been that too many have been more speculation than science, more influenced by bias than by balanced analysis. We have the tools and knowledge to do better. By embracing a data-driven, scenario-based approach, we can turn timeline forecasting from a source…
Read More » -
Quantum Tech and Espionage: What Every Researcher Must Know
To the untrained eye, espionage against scientists can be nearly invisible - it blends into everyday academic or business activity. But certain red flags and tactics surface again and again. Below is a consolidated list of common espionage methods (many from my own firsthand cases) used to target quantum tech…
Read More » -
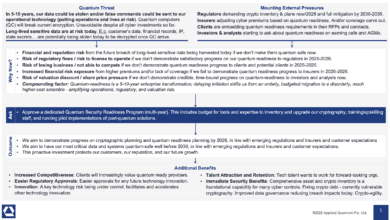
Securing Quantum Readiness Budget Now
From a CISO and business leadership perspective, the ask is clear: we need to secure budget and resources now to begin the multi-year journey of quantum-proofing our organization. This includes funding for risk assessments, cryptographic inventory tools, new encryption software/hardware, staff training or hiring, and pilot projects to start integrating…
Read More » -
Risk-Driven Strategies for Quantum Readiness When Full Crypto Inventory Isn’t Feasible
Given the practical challenges, organizations may need to begin their quantum-readiness journey with a risk-driven approach rather than a theoretically perfect one. The essence of this strategy is to focus limited resources where they matter most – addressing the highest quantum-vulnerability risks first and implementing interim safeguards for the rest.…
Read More » -
What is the Quantum Threat? A Guide for C‑Suite Executives and Boards
Boards do not need to dive into the scientific intricacies of qubits and algorithms, but they do need to recognize that this is a strategically important risk – one that can’t be simply delegated away. It requires the same level of governance attention as other enterprise-level risks like financial compliance,…
Read More » -
How CISOs Can Use Quantum Readiness to Secure Bigger Budgets (and Fix Today’s Problems)
Quantum readiness is not an exercise in science fiction – it’s a very practical program that yields benefits immediately. Regulators are pushing us all in this direction, which means boards are willing to fund it. The journey forces you to finally catalog your cryptographic assets and clean up long-standing weaknesses,…
Read More » -
CRQC Readiness Benchmark – Benchmarking Quantum Computers on the Path to Breaking RSA-2048
Benchmarking quantum capabilities for cryptography is both critical and challenging. We can’t rely on any single metric like qubit count to tell us how near we are to breaking RSA-2048. A combination of logical qubit count, error-corrected circuit depth, and operational speed must reach certain thresholds in unison. Existing benchmarks…
Read More » -
Quantum Readiness / PQC Migration Is The Largest, Most Complex IT/OT Overhaul Ever – So Why Wait?
Preparing for the quantum era is arguably the largest and most complicated digital infrastructure overhaul in history. Yes, far bigger than Y2K, because back in 1999 we didn’t have millions of network-connected “things” to worry about. Yet despite clear warnings and rapidly approaching milestones, far too many organizations still treat…
Read More » -
Why AI Cannot Break Modern Encryption
AI cannot break modern encryption. The reasons are fundamental: Mathematical Hardness, Cryptographic Design, Empirical Track Record, Quantum Contrast, Expert Consensus.
Read More » -
Q-Day Revisited – RSA-2048 Broken by 2030: Detailed Analysis
It’s time to mark a controversial date on the calendar: 2030 is the year RSA-2048 will be broken by a quantum computer. That’s my bold prediction, and I don’t make it lightly. In cybersecurity circles, the countdown to “Q-Day” or Y2Q (the day a cryptographically relevant quantum computer cracks our…
Read More » -
Cryptographic Inventory Vendors and Methodologies
Achieving a comprehensive cryptographic inventory often requires combining multiple tools and methodologies. Each solution above has blind spots: one might excel at catching code-level issues but miss network usage, another might see network traffic but miss dormant code, etc. Organizations starting a crypto inventory (especially as part of PQC readiness)…
Read More » -
What Is Q-Day (Y2Q)?
Q-Day, sometimes called “Y2Q” or the “Quantum Apocalypse”, refers to the future moment when a quantum computer becomes powerful enough to break modern encryption algorithms. In other words, it’s the day a cryptographically relevant quantum computer (CRQC) can crack the public-key cryptography (like RSA or ECC) that underpins our digital…
Read More » -
Quantum Readiness Assessment
A Quantum Readiness Assessment (QRA) is an in-depth review of an organization’s preparedness for the advent of quantum computing - especially its ability to withstand or adapt to the "quantum threat" posed by quantum computers that could render current cryptography obsolete. In practical terms, a QRA examines how an organization’s…
Read More » -
The Enormous Energy Cost of Breaking RSA‑2048 with Quantum Computers
The energy requirements for breaking RSA-2048 with a quantum computer underscore how different the post-quantum threat is from conventional hacking. It’s not just about qubits and math; it’s about megawatts, cooling systems, and power grids. Today, that reality means only the most potent actors would even contemplate such attacks, and…
Read More » -
Breaking RSA Encryption: Quantum Hype Meets Reality (2022-2025)
To put it plainly, if you encrypted a message with an RSA-2048 public key today, no one on Earth knows how to factor it with currently available technology, even if they threw every quantum computer and supercomputer we have at the task. That may change in the future – perhaps…
Read More »